Neural-IMLS: Self-supervised Implicit Moving Least-Squares Network for Surface Reconstruction
Abstract
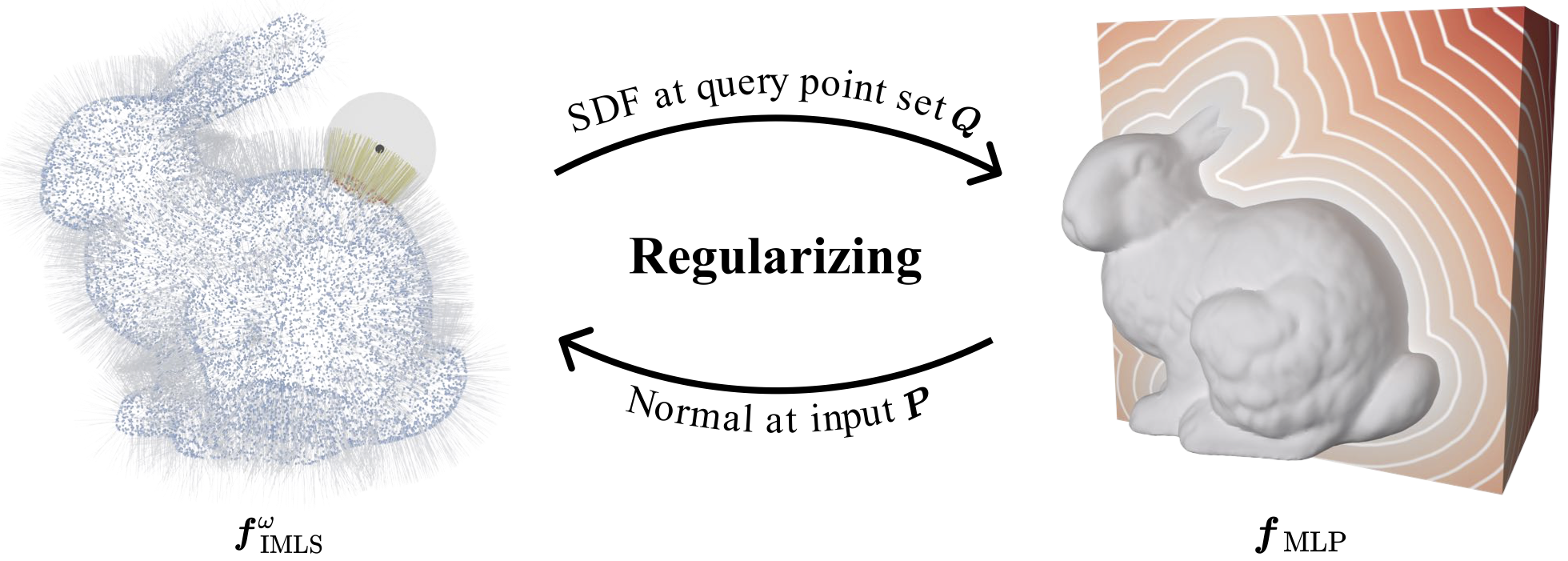
Surface reconstruction is a challenging task when input point clouds, especially real scans, are noisy and lack normals. Observing that the Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) and the implicit moving least-square function (IMLS) provide a dual representation of the underlying surface, we introduce Neural-IMLS , a novel approach that directly learns a noise-resistant signed distance function (SDF) from unoriented raw point clouds in a self-supervised manner. In particular, IMLS regularizes MLP by providing estimated SDFs near the surface and helps enhance its ability to represent geometric details and sharp features, while MLP regularizes IMLS by providing estimated normals. We prove that at convergence, our neural network produces a faithful SDF whose zero-level set approximates the underlying surface due to the mutual learning mechanism between the MLP and the IMLS. Extensive experiments on various benchmarks, including synthetic and real scans, show that Neural-IMLS can reconstruct faithful shapes even with noise and missing parts. The source code can be found at URL.
Cite
@ARTICLE{neuralimls2023wang,
author={Wang, Zixiong and Wang, Pengfei and Wang, Pengshuai and Dong, Qiujie and Gao, Junjie and Chen, Shuangmin and Xin, Shiqing and Tu, Changhe and Wang, Wenping},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics},
title={Neural-IMLS: Self-supervised Implicit Moving Least-Squares Network for Surface Reconstruction},
year={2023},
volume={},
number={},
pages={1-16},
doi={10.1109/TVCG.2023.3284233}
}